The Soroban, also known as the Japanese abacus, is an ancient calculating tool that has been used for centuries. It is a device that allows users to perform mathematical calculations through the manipulation of beads on rods. Here’s a complete guide to understanding and using the Soroban
Structure
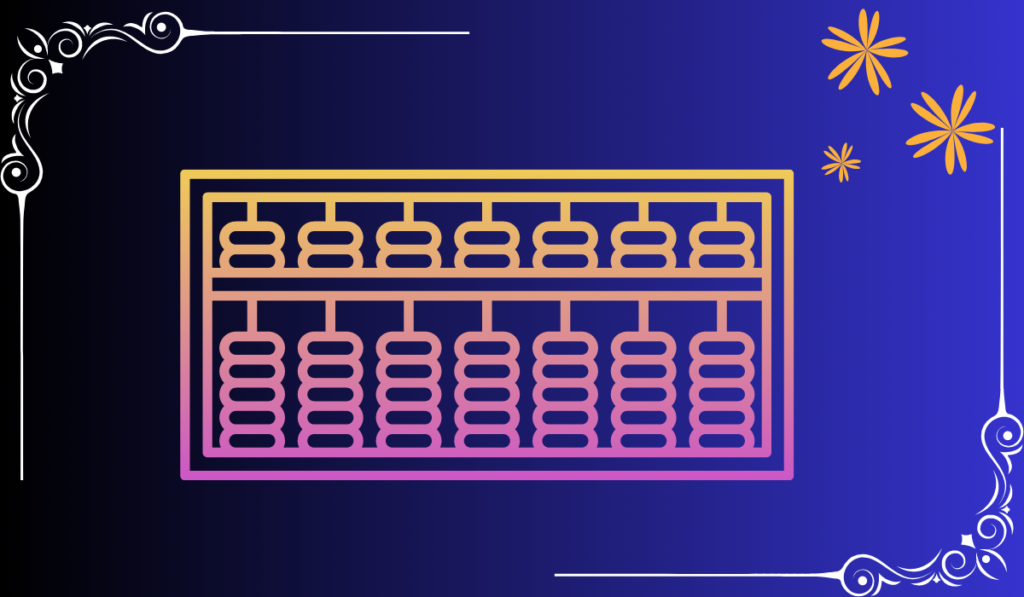
The Japanese abacus, is a calculating tool with a specific structure designed to facilitate numerical calculations. Its structure consists of a rectangular frame with multiple vertical rods or columns. The number of columns may vary depending on the specific Soroban model or the level of calculation complexity. Typically, a Soroban has either 13 or 21 columns.
Each column on the Japanese abacus represents a specific place value, starting from the right side. The rightmost column represents the units, followed by columns representing tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on. The columns are usually grouped into sets of five, with each set separated by a horizontal bar to aid in visually organizing the digits.
Within each column, there are beads that can be moved up and down. The Soroban generally has one or two beads on the upper deck and four beads on the lower deck. The beads on the upper deck represent the value 5, while the beads on the lower deck represent the values 1, 10, 100, and 1000, from bottom to top, respectively.
By moving the beads up and down the rods, users can represent and manipulate numbers. Moving a bead towards the center of the frame adds its value, while moving it away from the center subtracts its value. This physical manipulation of beads allows for efficient and accurate numerical calculations.
The structure of the Soroban provides a clear visual representation of place value, making it easier for users to perform calculations and keep track of numbers during arithmetic operations. The systematic arrangement of columns and beads allows for efficient addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, with carrying and borrowing techniques employed to ensure accurate results.
Overall, the structure of the Soroban is designed to provide a practical and intuitive means of performing calculations, making it a valuable tool for mental arithmetic and mathematical skill development.
Bead Manipulation
Bead manipulation is at the core of using the Soroban effectively for numerical calculations. The Soroban consists of vertical rods or columns, each containing beads that can be moved up and down. Understanding how to manipulate these beads is key to performing accurate calculations. Here’s a closer look at bead manipulation on the Soroban
Bead Values
Each column of the Soroban has specific bead values. The upper deck of beads represents the value 5, while the lower deck has beads representing the values 1, 10, 100, and 1000, from bottom to top.
Addition
To perform addition, beads are moved from right to left. If a bead is moved towards the center, its value is added to the total. When the value reaches or exceeds 5, a carry-over occurs to the next column.
Subtraction
Subtraction is done by moving beads from left to right. If a bead is moved away from the center, its value is subtracted from the total. If borrowing is necessary (when a lower-value bead is moved away and the higher-value bead is not present), beads are borrowed from the next column.
Carrying and Borrowing
Carrying and borrowing involve transferring beads between columns to maintain accurate calculations. Carrying occurs when the value in a column exceeds the bead’s maximum value, resulting in a bead being moved to the left. Borrowing happens when the value in a column is insufficient, requiring a bead to be borrowed from the next column to the right.
Multiplication and Division
Bead manipulation techniques vary for multiplication and division calculations on the Soroban, often involving specific movements and procedures to achieve accurate results. These techniques require practice and familiarity with multiplication and division principles.
Mastering bead manipulation on the Soroban involves developing hand-eye coordination, numerical visualization, and mental arithmetic skills. With practice, users become more proficient in swiftly moving beads, accurately representing numbers, and performing calculations efficiently on the Soroban, unlocking its potential for rapid mental calculations and improved numerical fluency.
Number Representation
Number representation on the Soroban is a fundamental aspect of using this calculating tool effectively. The Soroban’s structure allows for clear and concise representation of numbers, aiding in accurate calculations. Here’s an exploration of number representation on the Soroban:
Place Value
Each column on the Japanese Abacus represents a specific place value, starting from the right side. The rightmost column represents the units, followed by columns for tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on. This organization allows for easy visualization and manipulation of numbers with different place values.
Beads
Beads on the Soroban are used to represent different numerical values. The upper deck beads typically represent the value 5, while the lower deck beads represent the values 1, 10, 100, and 1000, from bottom to top, respectively. By manipulating these beads, users can accurately represent and calculate numbers.
Bead Position
The position of beads on the Soroban determines their contribution to the overall value. Beads moved towards the center of the frame add their respective values, while beads moved away from the center subtract their values. The physical movement of beads corresponds to the numerical operations being performed.
Visualization
Number representation on the Soroban requires users to visualize and mentally manipulate numbers. By looking at the arrangement of beads across the columns, users can quickly determine the numerical value represented by the Soroban configuration.
Understanding number representation on the Soroban allows users to accurately perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. By visualizing and manipulating beads to reflect numerical values, users can effectively perform calculations and achieve precise results.
Mastering number representation on the Soroban involves practice and familiarity with the Soroban’s structure, bead values, and place value concepts. With time and experience, users can develop a strong numerical intuition and fluency that enhances their mental arithmetic abilities and calculation speed on the Soroban.
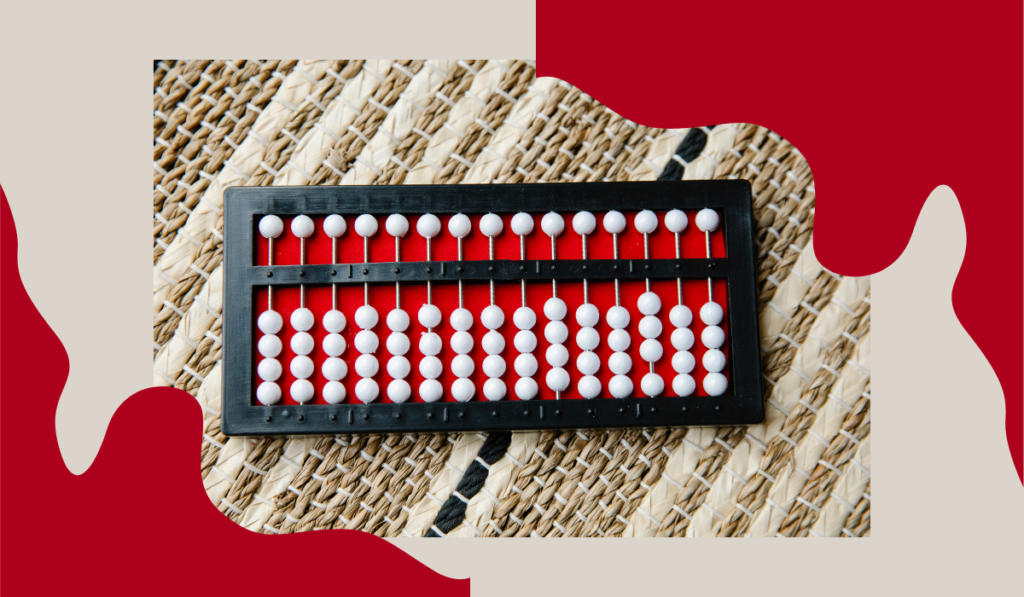

Practicing Soroban
Practicing the Japanese abacus, is essential for developing proficiency in its usage and harnessing its benefits for mental arithmetic and mathematical skills. Here’s a look at how to practice Soroban effectively:
Basics and Techniques
Start by familiarizing yourself with the structure and bead manipulation techniques of the Soroban. Learn how to represent numbers, perform basic operations, and understand carrying and borrowing concepts.
Number Visualization
Develop the ability to visualize numbers on the Soroban. Practice mentally visualizing a given number and representing it accurately on the Soroban, and vice versa.
Drill Exercises
Engage in drill exercises that involve repetitive calculations to build speed and accuracy. Begin with simple addition and subtraction problems and gradually progress to more complex calculations.
Speed Drills
Set a timer and challenge yourself to complete a set of calculations within a specific time limit. This helps improve mental agility, calculation speed, and accuracy.
Advanced Techniques
Explore advanced Soroban techniques such as multiplication, division, square roots, and more. These techniques require practice and mastery but significantly enhance mental calculation abilities.
Regular Practice
Dedicate regular time to practice the Soroban consistently. Consistency is key to building proficiency and maintaining your mental arithmetic skills.
challenge Yourself
Set personal goals and challenges to push yourself further. Attempt complex calculations, explore new techniques, and aim for greater speed and accuracy.
Practicing the Soroban regularly helps improve concentration, memory, and overall mental math abilities. It enhances numerical fluency, fosters critical thinking, and promotes a deeper understanding of numbers and arithmetic operations. Embrace the Soroban as a powerful tool for mental calculation and enjoy the rewards of its practice and application.
Benefits of Soroban
The Japanese abacus, offers numerous benefits that contribute to the development of mental arithmetic skills, numerical fluency, and cognitive abilities. Here are some key benefits of using the Soroban
Mental Calculation
Regular practice with the Soroban improves mental calculation abilities. Users learn to perform complex calculations in their minds, enhancing speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
Numerical Fluency
Manipulating beads on the Soroban strengthens number sense and fluency. Users develop a deeper understanding of numerical relationships, place value, and arithmetic operations.
Concentration and Focus
Using the Soroban requires concentration and focus. By engaging with the beads and performing calculations, users sharpen their attention and develop stronger concentration skills.
Memory Enhancement
Soroban practice enhances memory skills as users mentally visualize numbers and recall manipulation techniques. This aids in memorizing mathematical facts and strategies.
Problem-Solving Skills
The Soroban fosters problem-solving abilities by encouraging users to apply mathematical concepts to real-life situations and word problems. It promotes logical thinking and analytical reasoning.
Spatial Awareness
Manipulating the beads on the Soroban involves spatial reasoning. Users develop a sense of spatial awareness and gain proficiency in visualizing numbers and their relationships.
Increased Confidence
As proficiency in Soroban improves, users gain confidence in their mathematical abilities. This confidence extends to other areas of learning and problem-solving.
Cultural Appreciation
Learning and practicing the Japanese Abacus provides a cultural connection to Japan and its rich mathematical heritage. It promotes appreciation for different calculation methods and historical mathematical tools.
Mental Agility
practice challenges the mind and promotes mental agility. Users become more flexible in their thinking, adapt to various calculation scenarios, and develop quick mental calculation strategies.
Transferable Skills
Skills acquired through practice, such as concentration, problem-solving, and mental calculation, can be applied to other areas of life, including academics, professional endeavors, and everyday tasks.
The Soroban offers a holistic approach to developing mathematical skills, cognitive abilities, and mental agility. Its benefits extend beyond calculation proficiency, contributing to overall cognitive development and a deeper understanding of numbers and arithmetic operations.
Modern Usage
While it has a rich historical background, it continues to find relevance and usage in modern times. Here are some examples of how the Soroban is used today:
Mental Arithmetic Training
The Soroban is widely used as a tool for mental arithmetic training. It helps individuals develop and enhance their mental calculation abilities, improving speed, accuracy, and numerical fluency.
Math Education
In some educational settings, the Soroban is incorporated into math curricula to supplement traditional arithmetic teaching methods. It promotes a deeper understanding of numbers, place value, and arithmetic operations.
Brain Training
The Soroban is recognized for its cognitive benefits. It is often used in brain training programs and activities aimed at improving memory, concentration, attention span, and overall mental agility.
Skill Development
Professionals in various fields, such as accounting, finance, and engineering, use the Soroban to refine their numerical skills and improve accuracy in calculations.
Competition and Championships
Soroban competitions are held globally, allowing practitioners to showcase their skills and compete in mental arithmetic challenges. These events foster friendly competition and motivate individuals to continually improve their Soroban abilities.
Recreational Use
The Soroban is sometimes used as a recreational tool or hobby, providing mental stimulation and a source of enjoyment for enthusiasts of all ages.
Cultural Preservation
The Soroban plays a role in preserving cultural heritage. It serves as a symbol of Japan’s mathematical traditions and is often used in cultural exhibitions, festivals, and demonstrations to showcase its historical significance.
Digital Applications
With the advancement of technology, digital versions of the Soroban have emerged. Virtual Soroban apps and online platforms enable users to practice Soroban techniques digitally, providing an interactive and accessible learning experience.
Despite the prevalence of calculators and digital devices, the Soroban maintains its value as a tool for mental calculation, cognitive development, and cultural preservation. Its practical applications and cognitive benefits continue to make it relevant and useful in the modern world.
more on abacus
https://gemabacus.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=4191&action=edit
https://gemabacus.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=4186&action=edit
https://gemabacus.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=4181&action=edit

